In C#, IEnumerable and IQueryable are both interfaces that represent collections of data, but they have different characteristics and are used in different scenarios.
- IEnumerable<T> is the simplest form of collection interface in C#. It represents a forward-only cursor of elements.
- It is the most basic type for iterating over a collection of objects.
- It resides in the System.Collections namespace.
- It supports LINQ operations, but they are performed locally (in-memory). That means if you perform LINQ operations on an IEnumerable, all the data will be loaded into memory first, and then the query will be executed on that in-memory data.
- Generally used for querying data from in-memory collections like arrays, lists, or other IEnumerable implementations.
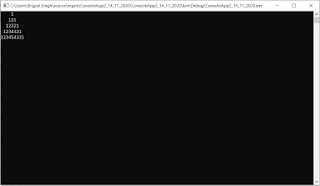
// IEnumerable example
IEnumerable<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
var result = numbers.Where(x => x > 2).ToList(); // LINQ query executed in memory
IQueryable:
- IQueryable<T> inherits from IEnumerable<T> but extends its capabilities by adding support for querying data from various data sources like databases (via LINQ to SQL, Entity Framework, etc.).
- It resides in the System.Linq namespace.
- It represents a query that can be executed on a specific data source.
- It allows for deferred execution, meaning the query is not executed until the result is actually enumerated.
- Queries written against IQueryable are translated into the native query language of the underlying data source (e.g., SQL for a relational database) and executed on the server-side, which can lead to better performance by only fetching the necessary data.
- Used for querying data from external data sources where the data may not reside entirely in memory.
Example:-
// Create a list of customer objects
List<Customer> customersList = new List<Customer>
{
new Customer { Id = 1, Name = "Alice", Age = 25 },
new Customer { Id = 2, Name = "Bob", Age = 30 },
new Customer { Id = 3, Name = "Charlie", Age = 18 },
};
// Create an IQueryable collection from the list
IQueryable<Customer> customersQuery = customersList.AsQueryable();
// Perform a LINQ query on the IQueryable collection
var result = customersQuery.Where(c => c.Age > 18).ToList();