The members of a class that can not be accessed without creating an instance for the class are called as instance members.
The members of a class that can be accessed without creating an instance and directly by using class name are called as static members.
The following example using instance member:
class Circle
{
float _PI = 3.14f;
int _Radius;
public Circle(int radius)
{
this._Radius = radius;
}
public float CalculateArea()
{
return this._PI * this._Radius * this._Radius;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Circle C1 = new Circle(5);
float area1 = C1.CalculateArea();
Console.WriteLine("Area {0}",area1);
Circle C2 = new Circle(6);
float area2 = C2.CalculateArea();
Console.WriteLine("Area {0}", area2);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
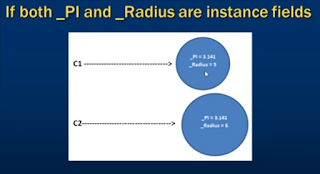
When using instance member _PI occupied memory every time when circle object are created.
The following example using static member:
class Circle
{
static float _PI;
int _Radius;
static Circle()
{
Circle._PI = 3.14f;
}
public Circle(int radius)
{
this._Radius = radius;
}
public float CalculateArea()
{
return Circle._PI * this._Radius * this._Radius;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Circle C1 = new Circle(5);
float area1 = C1.CalculateArea();
Console.WriteLine("Area {0}",area1);
Circle C2 = new Circle(6);
float area2 = C2.CalculateArea();
Console.WriteLine("Area {0}", area2);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
- When a class member includes a static modifier, the member is called as static member.
- When no static modifier present the member is called as non static member or instance member.
- Static members are invoked using class name, where as instance member are invoked instances (objects) of class.
- An instance member belongs to specific instance(object) of a class. If I create 3 objects of class, I will have 3 sets of instance member in memory, where as there will ever be only one copy of a static member, no matter how many instances of a class created.


No comments:
Post a Comment